Published January 3, 2023. Updated March 25, 2024. Open access. | Purchase book ❯ |
Rainbow Forest-Racer (Dendrophidion clarkii)
Reptiles of Ecuador | Serpentes | Colubridae | Dendrophidion clarkii
English common names: Rainbow Forest-Racer, Clark’s Forest-Racer, Green Forest-Racer.
Spanish common names: Corredora selvática arcoíris, corredora verde.
Recognition: ♂♂ 152.1 cmMaximum distance from the snout to the tip of the tail. Snout–vent length=90.9 cm. ♀♀ 155 cmMaximum distance from the snout to the tip of the tail. Snout–vent length=94.2 cm..1 Dendrophidion clarkii can be identified by presenting a combination of keeled dorsal scales arranged in 17 rows at mid-body, a black nuchal collar, dark crossbands with embedded pale ocelli, and conspicuously large eyes.1,2 This species presents ontogenetic variation in dorsal coloration (Fig. 1).3 In juveniles the black nuchal collar and reddish tail characteristic of adults is faint or lacking. Similar species in western Ecuador are D. graciliverpa and D. prolixum, but they differ from D. clarkii by lacking a black nuchal collar and dark crossbands with embedded pale ocelli.1
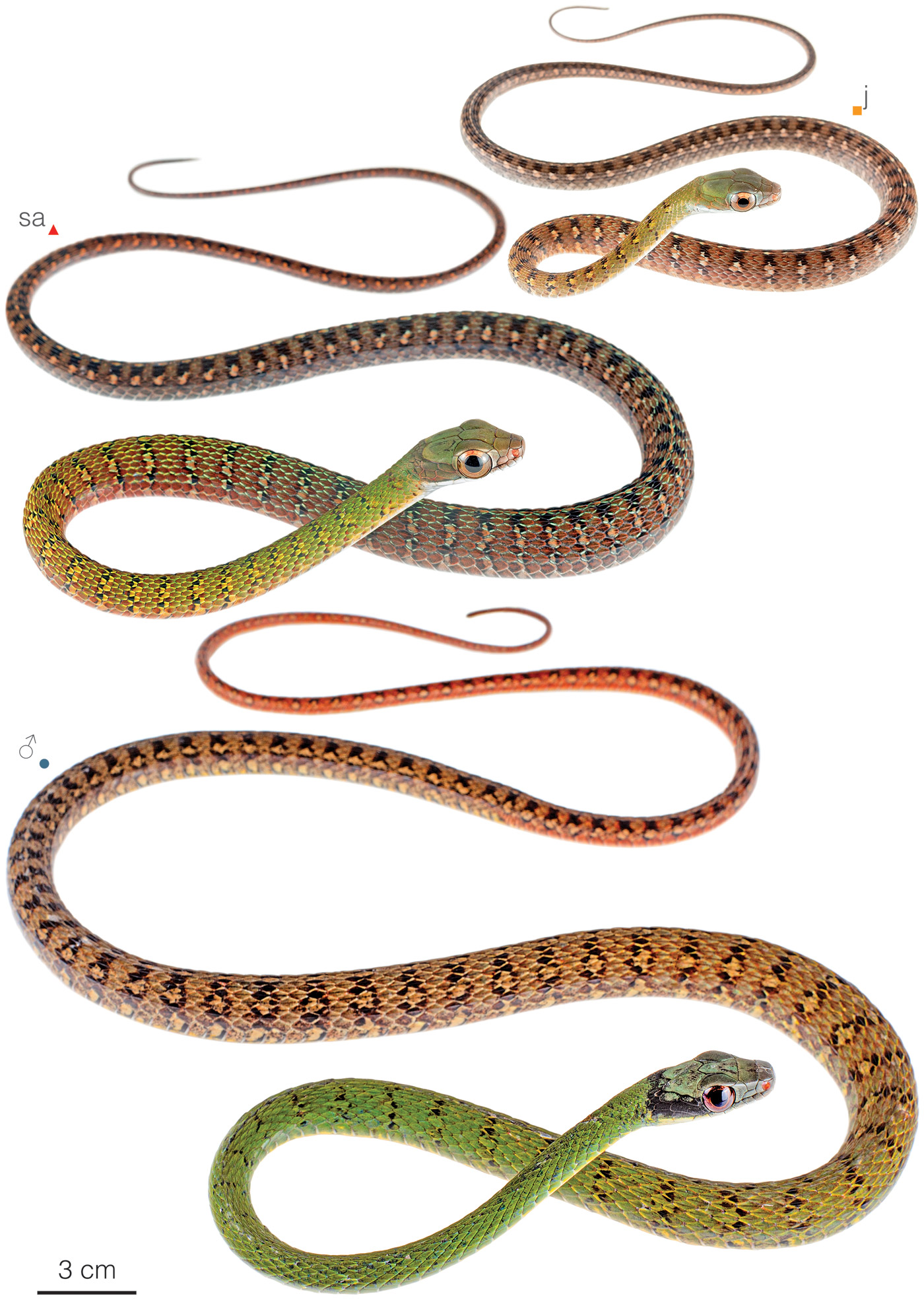

Figure 1: Individuals of Dendrophidion clarkii: Mashpi Lodge, Pichincha province, Ecuador (); Canandé Reserve, Esmeraldas province, Ecuador (); Morromico Reserve, Chocó department, Colombia (). j=juvenile.
Natural history: Dendrophidion clarkii is considered to be rare in Costa Rica,4 but is frequently encountered in forested environments in western Ecuador.5 The species occurs in old-growth rainforest as well as in pastures with scattered trees, cacao plantations, banana groves, and deforested areas where some riparian woodland or gallery forest remains.2,3 Snakes of this species are most often seen active at ground level or on low vegetation during the day,1 either basking or actively foraging on the leaf-litter.1,2 At night, they roost on low (less than 1.5 m above the ground) understory vegetation.5 Rainbow Forest-Racers are active hunters having an aglyphous dentition (meaning their teeth lack specialized grooves to deliver venom).1 Therefore, they ingest prey quickly to avoid them from escaping. The diet of D. clarkii includes primarily frogs of the genera Craugastor, Diasporus, and Pristimantis.6,7 The main defense mechanism of Rainbow Forest-Racers is to flee quickly, but they can also strike or shed-off parts of their tail.1 This species is oviparous. One gravid female contained 7 oviductal eggs1 and one nest in Ecuador consisted of 4 eggs.8
Conservation: Least Concern Believed to be safe from extinction given current circumstances..9,10 Dendrophidion clarkii is listed in this category because the species is widely distributed, especially in areas that have not been heavily affected by deforestation, like the Colombian Pacific coast, and it is unlikely to be declining fast enough to qualify for a more threatened category.9 The most important threat for the long-term survival of some populations is the loss of habitat due to large-scale deforestation.
Distribution: Dendrophidion clarkii is native to the Mesoamerican and Chocoan lowlands, from Costa Rica to southwestern Ecuador (Fig. 2).
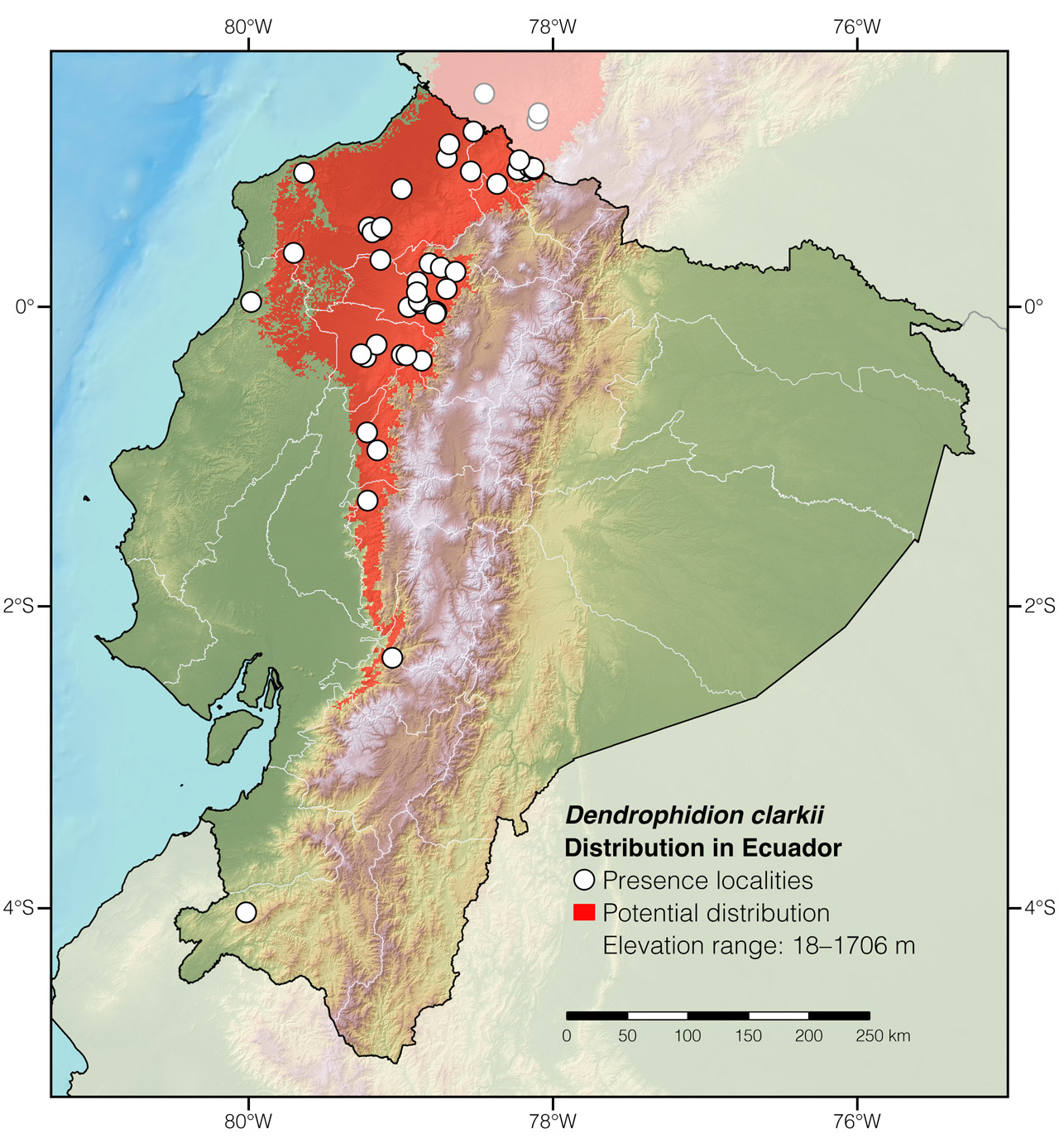
Figure 2: Distribution of Dendrophidion clarkii in Ecuador. See Appendix 1 for a complete list of the presence localities included in the map.
Etymology: The genus name Dendrophidion comes from the Greek words dendron (=tree) and ophidion (=small snake).11 The specific epithet clarkii honors American pathologist and researcher Herbert C. Clark (1877–1960), first director of the Gorgas Memorial Laboratory and instigator of the Panamanian snake census, which contributed immensely to the knowledge of the snake fauna of Panama.1
See it in the wild: Prime locations for the Rainbow Forest-Racer include the immediate environs of the towns of Mindo and Chical, where the snakes are most easily spotted sleeping on vegetation along water bodies at night or moving in pastures during sunny days.
Special thanks to Cheryl Vogt for symbolically adopting the Rainbow Forest-Racer and helping bring the Reptiles of Ecuador book project to life.
Click here to adopt a species.
Author: Alejandro ArteagaaAffiliation: Fundación Khamai, Reserva Arlequín, Ecoruta Paseo del Quinde km 56, Santa Rosa de Mindo, Pichincha 171202, Ecuador.
Photographers: Jose VieirabAffiliation: Tropical Herping (TH), Quito, Ecuador.,cAffiliation: ExSitu, Quito, Ecuador. and Sebastián Di DoménicodAffiliation: Keeping Nature, Bogotá, Colombia.
How to cite? Arteaga A (2023) Rainbow Forest-Racer (Dendrophidion clarkii). In: Arteaga A, Bustamante L, Vieira J (Eds) Reptiles of Ecuador: Life in the middle of the world. Available from: www.reptilesofecuador.com. DOI: 10.47051/COND1023
Literature cited:
- Cadle JE, Savage JM (2012) Systematics of the Dendrophidion nuchale complex (Serpentes: Colubridae) with the description of a new species from Central America. Zootaxa 3513: 1–50. DOI: 10.11646/zootaxa.3513.1.1
- Arteaga A, Bustamante L, Guayasamin JM (2013) The amphibians and reptiles of Mindo. Universidad Tecnológica Indoamérica, Quito, 257 pp.
- Lieb CS (1988) Systematic status of the Neotropical snakes D. dendrophis and D. nuchalis. Herpetologica 44: 162–175.
- Savage JM (2002) The amphibians and reptiles of Costa Rica, a herpetofauna between two continents, between two seas. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 934 pp.
- Field notes, Reptiles of Ecuador book project.
- Matthijs Hollanders, pers. comm.
- Leenders T (2019) Reptiles of Costa Rica: a field guide. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, 625 pp.
- Photo by Sebastián Vizcarra.
- Köhler G, Lamar W (2017) Dendrophidion clarkii. The IUCN Red List of threatened species. Available from: www.iucnredlist.org. DOI: 10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T203288A2763009.en
- Morales-Betancourt MA, Lasso CA, Páez VP, Bock BC (2005) Libro rojo de reptiles de Colombia. Instituto de Investigación de Recursos Biológicos Alexander von Humboldt, Bogotá, 257 pp.
- Brown RW (1956) Composition of scientific words. Smithsonian Books, Washington D.C., 882 pp.
Appendix 1: Locality data used to create the distribution map of Dendrophidion clarkii in Ecuador (Fig. 2). Go to the section on symbols and abbreviations for a list of acronyms used.
| Country | Province | Locality | Source |
| Colombia | Nariño | Altaque, 1 km SE of | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Colombia | Nariño | La Guayacana | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Colombia | Nariño | Reserva Río Ñambí | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Colombia | Valle del Cauca | Campamento Cartón Colombia | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Colombia | Valle del Cauca | Cisneros | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Bolívar | San Luis de Pambil | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Chical | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Chical–La Primavera road | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Chical, 6 km E of | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Maldonado | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Maldonado, 1 km N of | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Peñas Blancas | Reptiles of Ecuador book database |
| Ecuador | Carchi | Sendero Awa | Yánez-Muñoz 2009 |
| Ecuador | Chimborazo | Valle del Chanchán | Lieb 1988 |
| Ecuador | Cotopaxi | El Jardín de los Sueños | Photo by Christophe Pellet |
| Ecuador | Cotopaxi | Yakusinchi | Photo by Jane Sloan |
| Ecuador | Esmeraldas | Alto Tambo, 3 km SE of | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Esmeraldas | Bilsa Biological Reserve | Ortega-Andrade et al. 2010 |
| Ecuador | Esmeraldas | Cachabi | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Esmeraldas | Canandé Biological Reserve | This work; Fig. 1 |
| Ecuador | Esmeraldas | Itapoa Reserve | Photo by Rául Nieto |
| Ecuador | Esmeraldas | Lote Rosero | Reptiles of Ecuador book database |
| Ecuador | Esmeraldas | Pulún | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Esmeraldas | Reserva Tesoro Escondido | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Esmeraldas | Río Sapayo | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Esmeraldas | San Mateo | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Paramba | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Reserva Los Cedros | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Río Chalguayacu | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Río Guayllabamba | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Imbabura | Vía a García Moreno | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Loja | Alamor | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Manabí | Cerro Pata de Pájaro | Arteaga et al. 2013 |
| Ecuador | Pichincha | Hacienda La Hesperia | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Pichincha | Kapari Lodge’s trails | Reptiles of Ecuador book database |
| Ecuador | Pichincha | Maquipucuna Reserve | Arteaga et al. 2013 |
| Ecuador | Pichincha | Mashpi Lodge | Yánez-Muñoz et al. 2009 |
| Ecuador | Pichincha | Milpe | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Pichincha | Milpe Bird Sanctuary | Photo by Jose Vieira |
| Ecuador | Pichincha | Mindo, 3.5 km NE of | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Pichincha | Pachijal | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Pichincha | Road to Mindo | Arteaga et al. 2013 |
| Ecuador | Pichincha | Séptimo Paraíso | Arteaga et al. 2013 |
| Ecuador | Pichincha | Yellow House Lodge | Arteaga et al. 2013 |
| Ecuador | Santo Domingo de los Tsáchilas | Alluriquín | Arteaga et al. 2013 |
| Ecuador | Santo Domingo de los Tsáchilas | Otongachi | Arteaga et al. 2013 |
| Ecuador | Santo Domingo de los Tsáchilas | Río Baba | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Santo Domingo de los Tsáchilas | Santo Domingo de los Colorados | Cadle & Savage 2012 |
| Ecuador | Santo Domingo de los Tsáchilas | Santo Domingo de los Colorados, 5–10 km SSW of | Cadle & Savage 2012 |