Published May 30, 2019. Updated December 26, 2023. Open access. | Purchase book ❯ |
Tumbesian Leaf-toed Gecko (Phyllodactylus kofordi)
Reptiles of Ecuador | Sauria | Phyllodactylidae | Phyllodactylus kofordi
English common names: Tumbesian Leaf-toed Gecko, Koford’s Leaf-toed Gecko.
Spanish common names: Geco tumbesino, salamanquesa de Koford.
Recognition: ♂♂ 9.3 cmMaximum distance from the snout to the tip of the tail. Snout–vent length=4.5 cm. ♀♀ 9.6 cmMaximum distance from the snout to the tip of the tail. Snout–vent length=4.6 cm..1 Phyllodactylus kofordi is easily distinguishable from other geckos occurring in the dry forests of southwestern Ecuador by having narrow and rounded digital disks and dorsal surfaces covered by densely packed tubercles that are strongly keeled, large, and trihedral (Fig. 1).1,2 The dorsal coloration is usually pale grayish brown with broad irregular dark blotches and a thin black postocular stripe that extends beyond the insertion of the forearms (Fig. 1).1 Phyllodactylus kofordi differs from P. reissii by having large tubercles on the dorsal aspect of the tail (absent in P. reissii).1
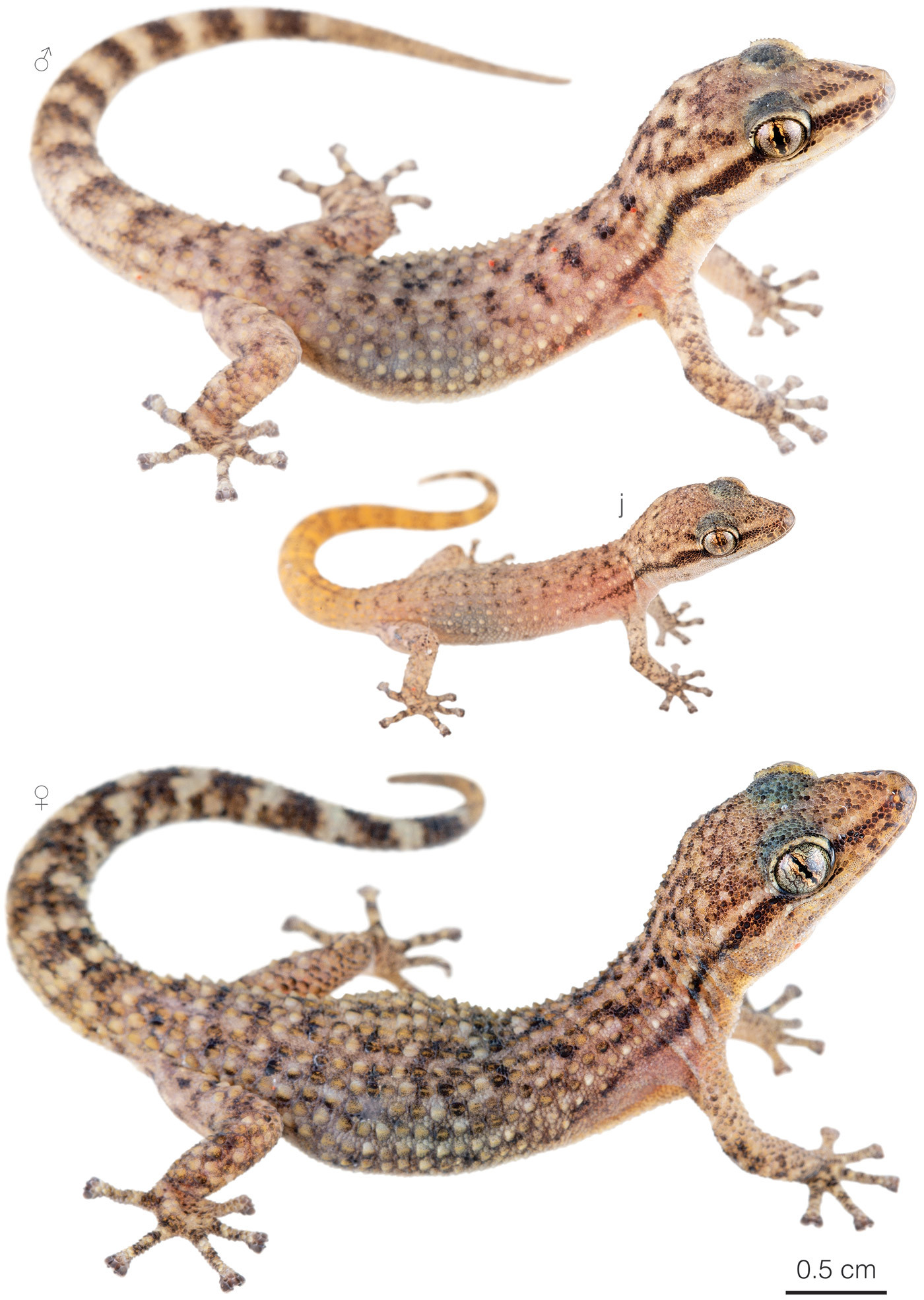

Figure 1: Individuals of Phyllodactylus kofordi from Bella María Grande, Loja province, Ecuador. j=juvenile.
Natural history: Phyllodactylus kofordi is a nocturnal and terrestrial to semiarboreal gecko that inhabits dry shrublands, deserts, and deciduous to semideciduous forests.1–4 During dry, clear nights, Tumbesian Leaf-toed Geckos forage at ground level or on rocks, boulders and shrubs up to 2.5 m above the ground.1–4 By daytime, they seek refuge in crevices, holes, leaf-litter, bark, debris, and under trash.1 Breeding takes place throughout the year, with clutches of a single egg laid in communal nesting sites, usually under rotting cacti alongside clutches of P. reissii.1 The diet in this species consists of insects smaller than 15 mm, including beetles, caterpillars, ants, flies, arachnids, pseudoscorpions, and hemipterans.5 In the presence of a disturbance, the typical escape tactic is to flee into crevices
Conservation: Least Concern Believed to be safe from extinction given current circumstances..6 Phyllodactylus kofordi is listed in this category because this species is widespread, thrives in human-modified environments and has not been shown conclusively to have undergone population declines. Although Tumbesian Leaf-toed Geckos are not considered a human commensal species, they do thrive in anthropic areas such as along roadsides and in rock walls.3
Distribution: Phyllodactylus kofordi is native to the Tumbesian lowlands of southwestern Ecuador and northwestern Perú (Fig. 2).
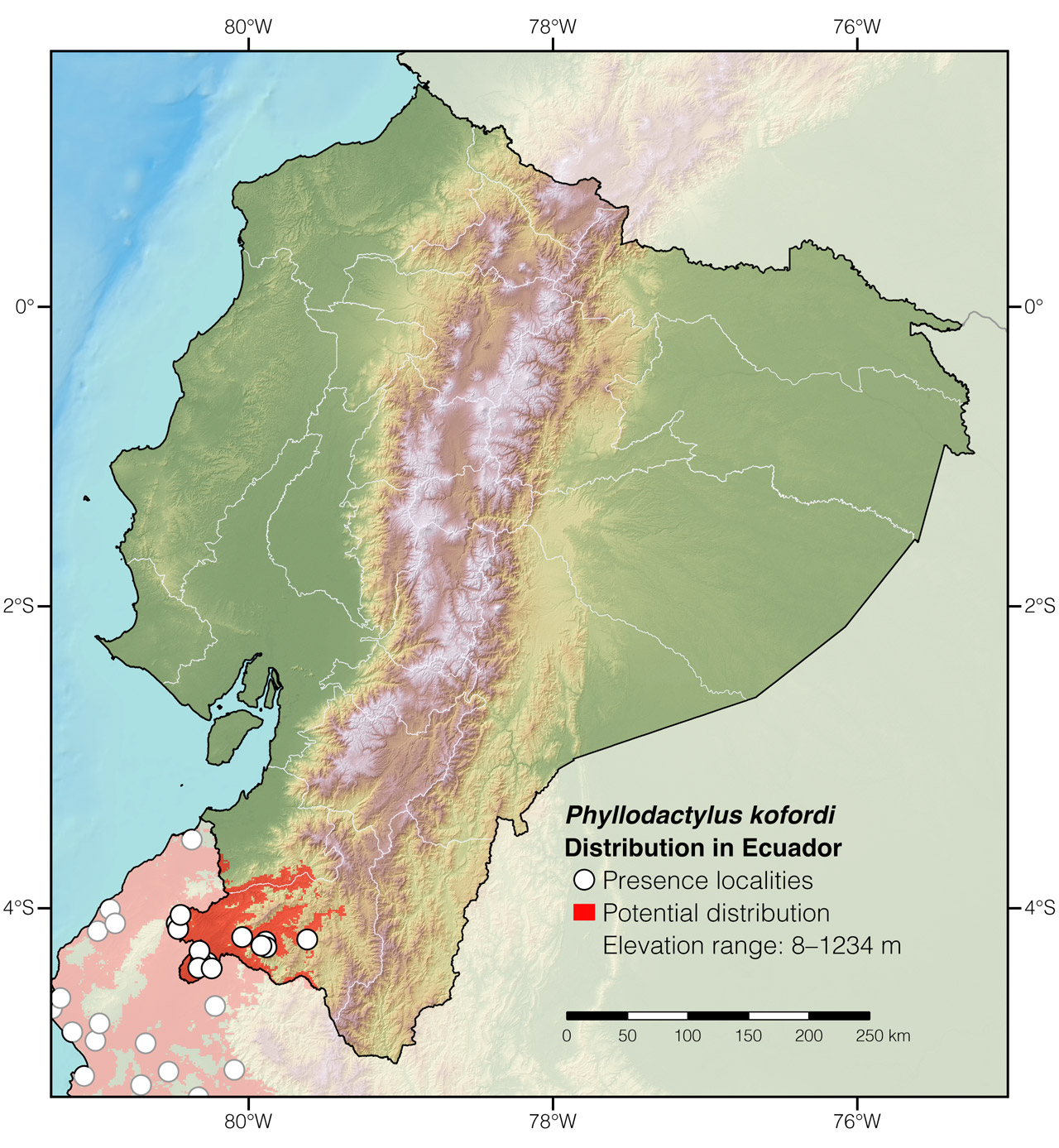
Figure 2: Distribution of Phyllodactylus kofordi in Ecuador. See Appendix 1 for a complete list of the presence localities included in the map.
Etymology: The generic name Phyllodactylus comes from the Greek words phyllon (=leaf) and daktylos (=finger),7 and refers to the leaf-shaped fingers characteristic of this group of geckos. The specific epithet kofordi honors Carl Koford (1915–1979), an American biologist who has greatly contributed to the knowledge of the reptilian fauna of Perú.1
See it in the wild: In Ecuador, Phyllodactylus kofordi is considered a locally common species in some areas. For example, these geckos are guaranteed sightings during night hikes along forest trails of Reserva Natural La Ceiba and Reserva Laipuna. The best time to look for lizards of this species is just after sunset.
Authors: Alejandro ArteagaaAffiliation: Fundación Khamai, Reserva Arlequín, Ecoruta Paseo del Quinde km 56, Santa Rosa de Mindo, Pichincha 171202, Ecuador. and Gabriela AguiarbIndependent researcher, Quito, Ecuador.
Photographer: Jose VieiracAffiliation: Tropical Herping (TH), Quito, Ecuador.,dAffiliation: ExSitu, Quito, Ecuador.
How to cite? Arteaga A, Aguiar G (2023) Tumbesian Leaf-toed Gecko (Phyllodactylus kofordi). In: Arteaga A, Bustamante L, Vieira J (Eds) Reptiles of Ecuador: Life in the middle of the world. Available from: www.reptilesofecuador.com. DOI: 10.47051/HTTS2397
Literature cited:
- Dixon JR, Huey RB (1970) Systematics of the lizards of the gekkonid genus Phyllodactylus of mainland South America. Los Angeles County Museum Contributions in Science 192: 1–78. DOI: 10.5962/p.241179
- Torres-Carvajal O, Carvajal-Campos A, Barnes CW, Nicholls G, Pozo-Andrade MJ (2013) A new Andean species of Leaf-toed Gecko (Phyllodactylidae: Phyllodactylus) from Ecuador. Journal of Herpetology 47: 384–390. DOI: 10.1670/12-017
- Field notes, Reptiles of Ecuador book project.
- Carillo de Espinoza N, Icochea J (1995) Lista taxonómica preliminar de los reptiles vivientes del Perú. Publicaciones del Museo de Historia Natural, Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos 49: 1–27.
- Huey RB (1979) Parapatry and niche complementarity of Peruvian desert geckos (Phyllodactylus): the ambiguous role of competition. Oecologia 38: 249–259. DOI: 10.1007/BF00345186
- Venegas P, Perez J, Aguilar C, Quiroz Rodriguez A (2016) Phyllodactylus kofordi. The IUCN Red List of threatened species. Available from: www.iucnredlist.org. DOI: 10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T48442821A48442826.en
- Brown RW (1956) Composition of scientific words. Smithsonian Books, Washington, 882 pp.
Appendix 1: Locality data used to create the distribution map of Phyllodactylus kofordi in Ecuador (Fig. 2). Go to the section on symbols and abbreviations for a list of acronyms used.
| Country | Province | Locality | Source |
| Ecuador | Loja | Bella María Grande | This work; Fig. 1 |
| Ecuador | Loja | Cabeza de Toro, 3.5 km NW of | Reptiles of Ecuador book database |
| Ecuador | Loja | Cazaderos | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Loja | La vertiente de Zapallal | Torres-Carvajal et al. 2014 |
| Ecuador | Loja | Mangahurco | Photo by Fausto Siavichay |
| Ecuador | Loja | Numbiaranga | Torres-Carvajal et al. 2013 |
| Ecuador | Loja | Portachuelo | Reptiles of Ecuador book database |
| Ecuador | Loja | Progreso | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Ecuador | Loja | Quebrada El Faique | Torres-Carvajal et al. 2013 |
| Ecuador | Loja | Reserva La Ceiba | Reptiles of Ecuador book database |
| Ecuador | Loja | Reserva Laipuna | Torres-Carvajal et al. 2013 |
| Ecuador | Loja | Vertiente de Zapallal | Torres-Carvajal et al. 2013 |
| Ecuador | Loja | Zapotillo | Mármol–Guijarro & Rodríguez-Guerra 2020 |
| Perú | Piura | Castilla | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Perú | Piura | Cerro Amotape | Dixon & Huey 1970 |
| Perú | Piura | Las Lomas, 3 km ENE of | Dixon & Huey 1970 |
| Perú | Piura | Lobitos, 30 mi S of | Dixon & Huey 1970 |
| Perú | Piura | Negritos | Dixon & Huey 1970 |
| Perú | Piura | Paita | Dixon & Huey 1970 |
| Perú | Piura | Palo Blanco | Vásquez Calle 2018 |
| Perú | Piura | Piura, 2 km W of | iNaturalist; photo examined |
| Perú | Piura | Pozas | Torres-Carvajal et al. 2014 |
| Perú | Piura | Puente de Máncora | Reptiles of Ecuador book database |
| Perú | Piura | Sullana | Dixon & Huey 1970 |
| Perú | Piura | Sullana, 40 km WNW of | Dixon & Huey 1970 |
| Perú | Piura | Talara | Dixon & Huey 1970 |
| Perú | Tumbes | Cancas, 1.2 km S of | Dixon & Huey 1970 |
| Perú | Tumbes | Puerto Pizarro, 1 km E of | Dixon & Huey 1970 |
| Perú | Tumbes | Quebrada Seca | Dixon & Huey 1970 |